
Certain observations obtained by Rutherford contradicted Thomson's atomic hypothesis. He wrapped a fluorescent zinc sulphide screen around thin gold foil to investigate deflection generated by particles. In his experiment, Rutherford focused on high-energy particle streams from a radioactive source at a thin sheet of gold (100 nm thickness). Rutherford carried out an experiment in which he bombarded a thin sheet of gold foil with -particles and then analyzed track of these particles after they collided with gold foil. If nucleus of an atom is unbalanced, that is, if number of protons and neutrons differs, atom is unstable. It accomplishes this by emitting particles such as alpha and beta. Process through which unstable nucleus of an atom loses energy by emitting particles is known as radioactivity.
However, findings of subsequent trials contradicted its assertions. Atomic model of Thomson was successful in explaining atom's general neutrality. Assumption that atom's mass is equally distributed across atom is key feature of this model. As a result, watermelon model, plum pudding model, and raisin pudding model are all names for this model. Electrons are encased in this sphere to create stable electrostatic configuration possible.Ībove illustration resembles a chopped watermelon with electrons representing seeds. He proposed that atom is shaped like sphere with radius of around 10 -10m with uniformly distributed positive charge.
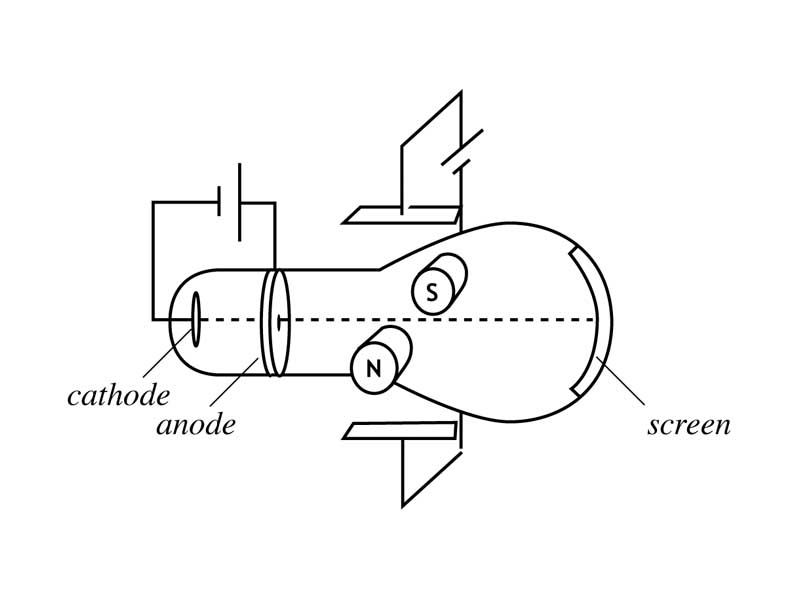
THOMSON CATHODE RAY EXPERIMENT EXPLANATION SERIES
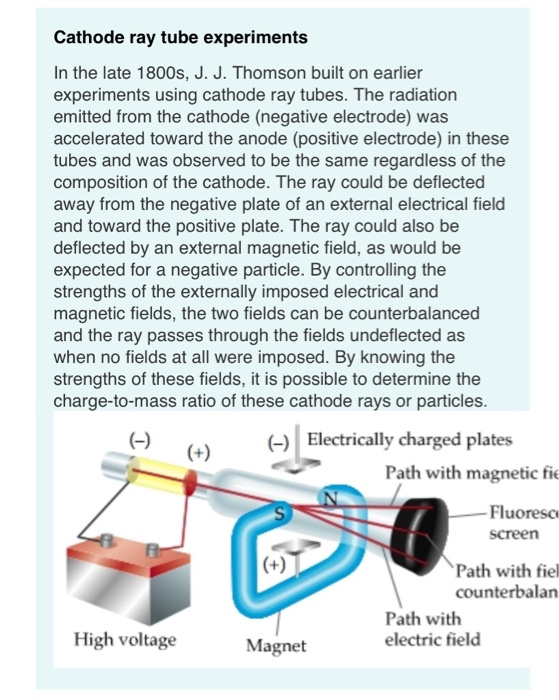
Thomson proposed first in a series of atomic models in 1898. Cathode rays were found to be negatively charged as a result of this. He discovered that when he used charged metal plates, cathode rays bent away from negative plate and towards positive plate. He used fluorescent coated tube instead of electrometer at one end of Cathode Ray Tube, which would illuminate when cathode ray hit it. He now placed a negatively charged metal plate on one side of cathode rays to allow them to pass through anode and a positively charged metal plate on the other. He then performed a second experiment to determine whether charge carried by cathode rays was negative or positive. He observed that electrometers ceased measuring electric charge after first experiment. Two microscopic perforations in metal led to an electrometer that could measure a modest electric charge. On the other end of his cathode ray tube, he created a metal cylinder. Thompson performed first cathode ray tube experiment to demonstrate that rays released by an electron cannon are inseparable from latent charge. Scientists have defined this as one atomic mass unit (amu) or one Dalton.
Protons and neutrons have same mass (approx.), nearly 1.67 × 10 -24 grams.
Components of Atom are Electrons and compact nucleus of Protons and Neutrons.Įlectric charge of Atom is zero, or ion charge. It's also smallest unit of matter with chemical element features. Atom is smallest unit of matter that may be divided without releasing electrically charged particles.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
